“We shall not cease from exploration
and the end of all our exploring
will be to arrive where we started
And know the place for the first time”
T. S. Eliot, No. 4 of 4 Quartets, 1943
One of the charity’s key objectives is
“To engage with the key stakeholders involved in the design and agreement of clinical definition sets for each stage of the integrated care pathway for Covid & Long Covid”
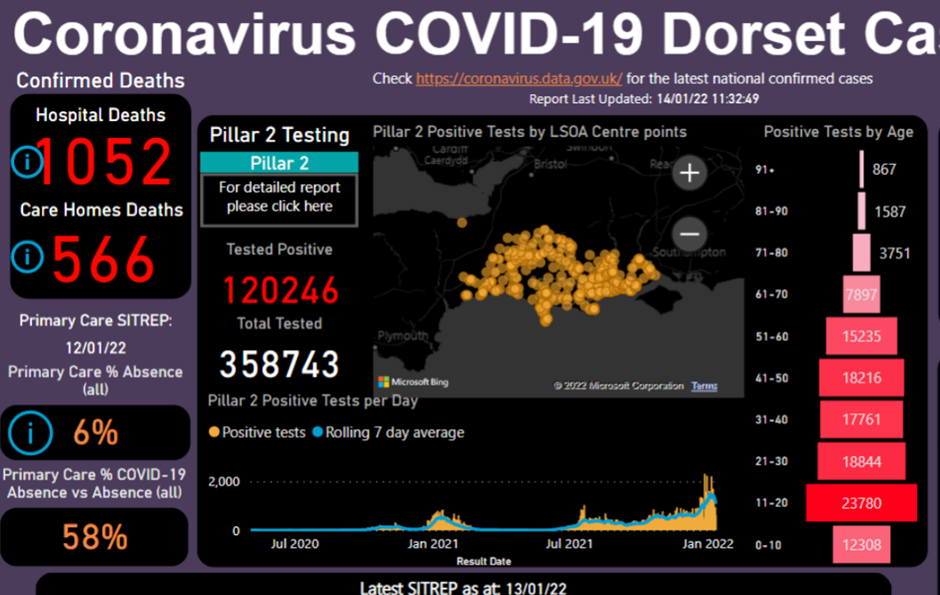
The Dorset COVID 19 Dashboard is a good example of informatics applied to Covid 19 and is summarised on our Provider Spotlight page here
https://breatheon.co.uk/index.php/providers
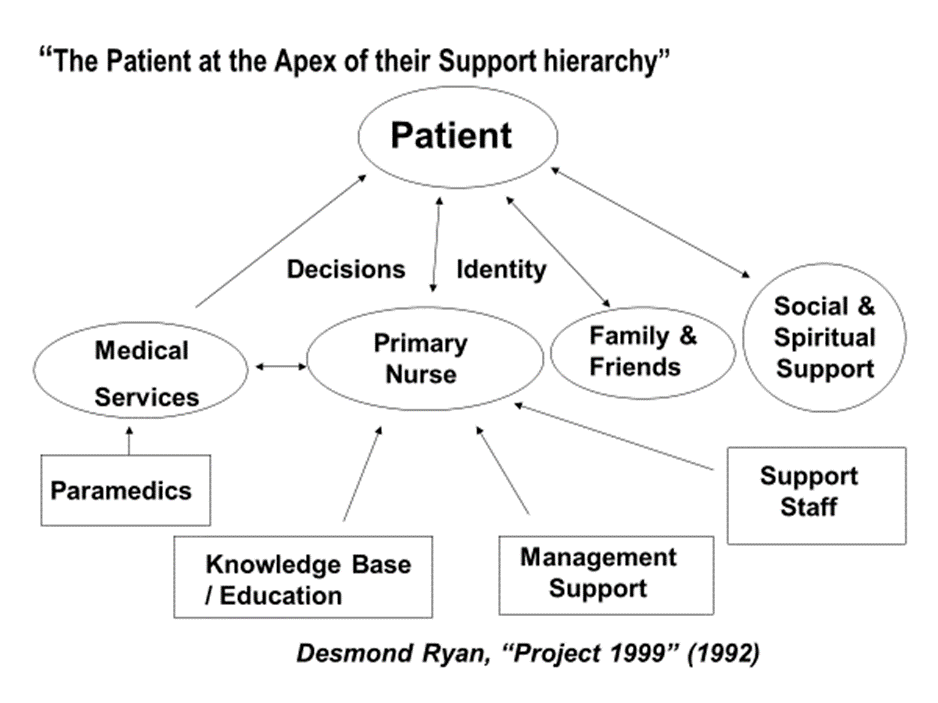
A Patient Focused Approach
The charity is committed to taking a patient’s perspective at all times
(The diagram below was produced by Desmond Ryan in 1992 as part of a series of studies on behalf of the Department of Health in England in preparation for the Project 2000 workforce plan)
In order to understand the health needs of a population, you must firstly understand the level, range and complexity of those needs from a patient perspective.
Short Form Health Survey
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SF-36
The SF36 Health Survey is a 36-item, patient-reported survey of patient health. The SF-36 is a measure of health status and an abbreviated variant of it, the SF-6D, is commonly used in health economics as a variable in the quality-adjusted life year calculation to determine the cost-effectiveness of a health treatment.
The SF-36 consists of eight scaled scores, which are the weighted sums of the questions in their section. Each scale is directly transformed into a 0-100 scale on the assumption that each question carries equal weight. The lower the score the more disability. The higher the score the less disability i.e., a score of zero is equivalent to maximum disability and a score of 100 is equivalent to no disability.
The eight sections of an SF36 are:
- vitality
- physical functioning
- bodily pain
- general health perceptions
- physical role functioning
- emotional role functioning
- social role functioning
- mental health or emotional wellbeing
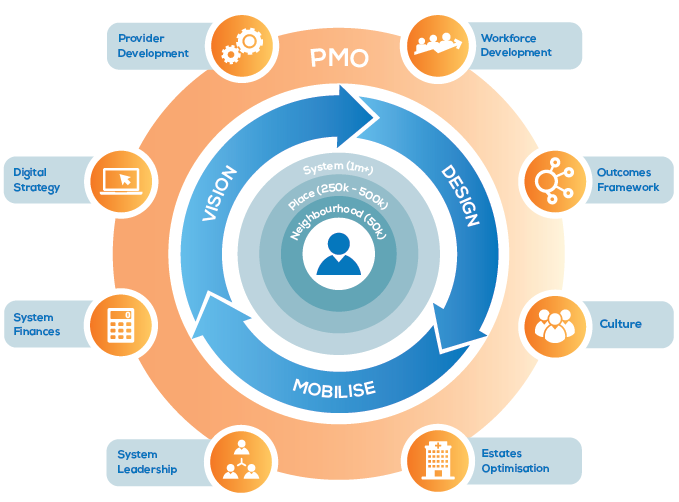
NHS Integrated Care System Development
https://www.sbs.nhs.uk/article/15066/Integrated-Care-System-Development
Naturalistic Enquiry & Evaluative Criteria
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256294652_Naturalistic_Inquiry
Lincoln and Guba posit that trustworthiness of a research study is important to evaluating its worth. Trustworthiness involves establishing:
- Credibility – confidence in the ‘truth’ of the findings
- Transferability – showing that the findings have applicability in other contexts
- Dependability – showing that the findings are consistent and could be repeated
- Confirmability – a degree of neutraility or the extent to which the findings of a study are shaped by the respondents and not researcher bias, motivation, or interest
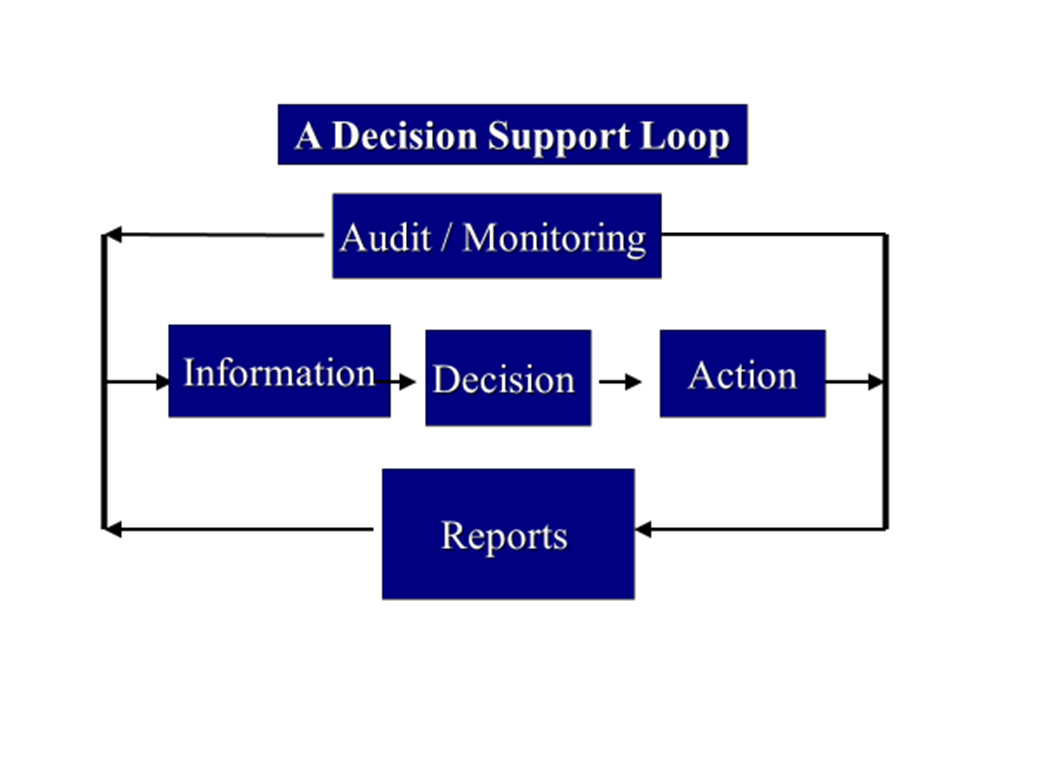
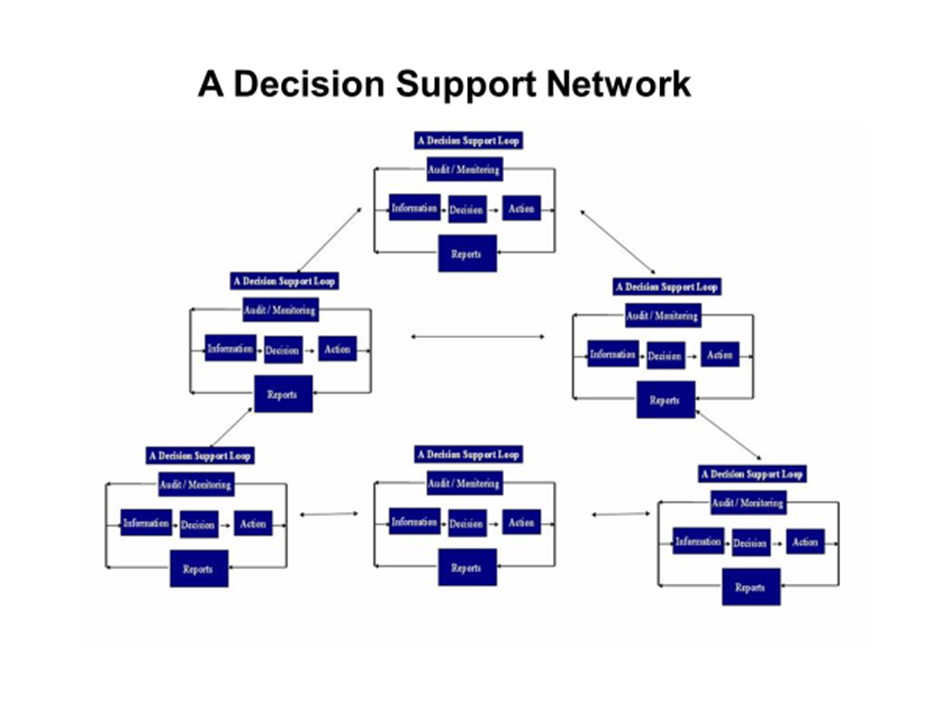
A Decision Support System (DSS)
…is an information system that supports business or organisational decision-making activities.
DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization (usually mid and higher management) and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e., unstructured and semi-structured decision problems.
Decision support systems can be either fully computerised or manually operated, or a combination of both.
Managed Clinical Networks
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20829865
Managed clinical networks (MCNs) are self-supporting groups of professionals working together to ensure cross-speciality sharing of patients and expertise. They are a strong mechanism for ensuring that patients receive the care they need in a timely fashion from the most suitable professional in the network area. This short article in this link will explain how they work and how they can work.
The McCumber Cube
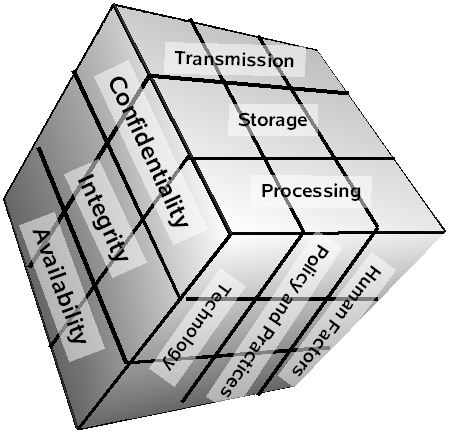
In 1991, John McCumber created a model framework for establishing and evaluating information security (information assurance) programs, now known as The McCumber Cube. This security model is depicted as a three-dimensional Rubik’s Cube-like grid.
The concept of this model is that, in developing information assurance systems, organizations must consider the interconnectedness of all the different factors that impact them. To devise a robust information assurance program, one must consider not only the security goals of the program (see below), but also how these goals relate specifically to the various states in which information can reside in a system and the full range of available security safeguards that must be considered in the design. The McCumber model helps one to remember to consider all important design aspects without becoming too focused on any one in particular (i.e., relying exclusively on technical controls at the expense of requisite policies and end-user training).
Politics Matters
The Ideal
The actualite…
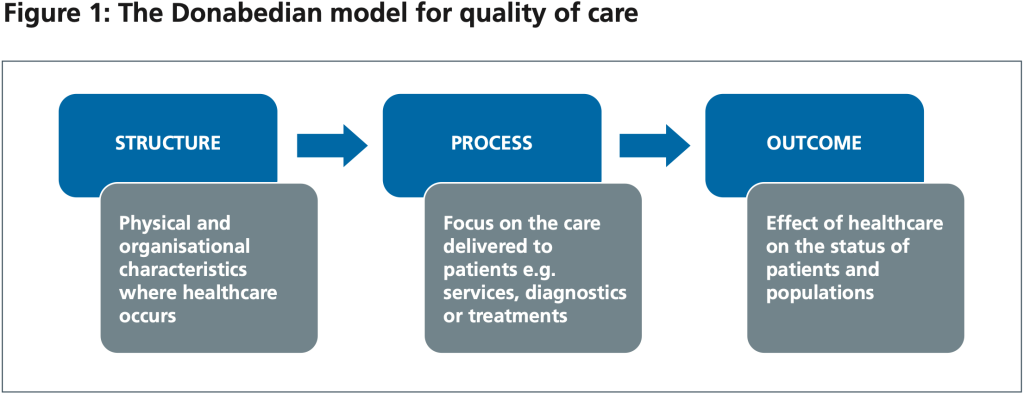
Avedis Donabedian and The Birth of Healthcare Quality Assurance
https://healthcaremarketreview.com/avedis-donabedian-and-the-birth-of-healthcare-quality-assurance
https://healthcaremarketreview.com/avedis-donabedian-and-the-birth-of-healthcare-quality-assurance/
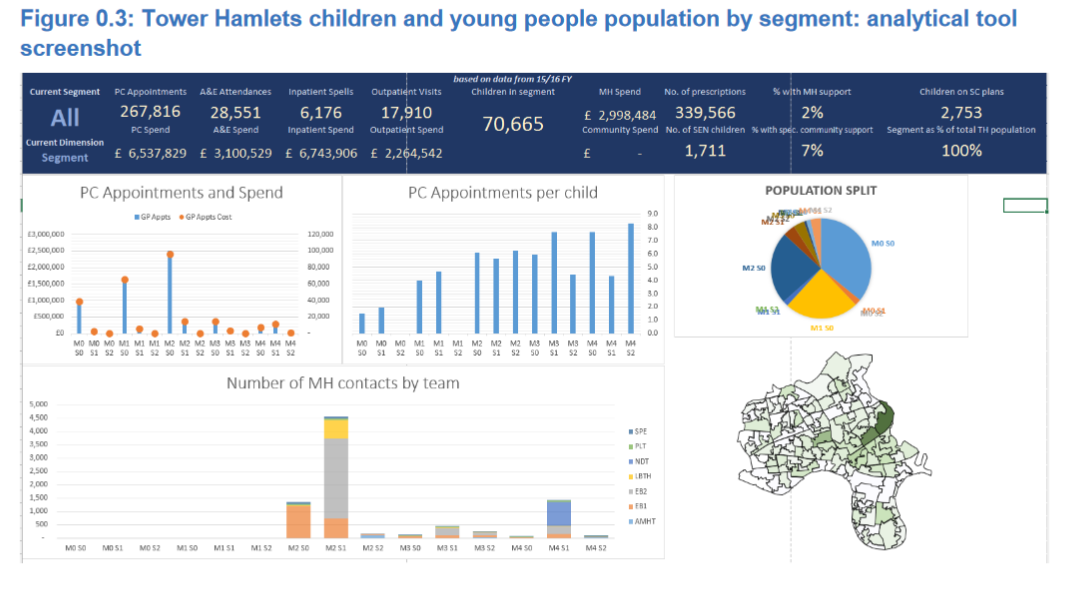
The Apollo Project
The 2017 Tower Hamlets Apollo Project delivered a proof of concept that it was possible to combine existing health and social care information sources from multiple agencies and combine them into a very useful local population health information tool.
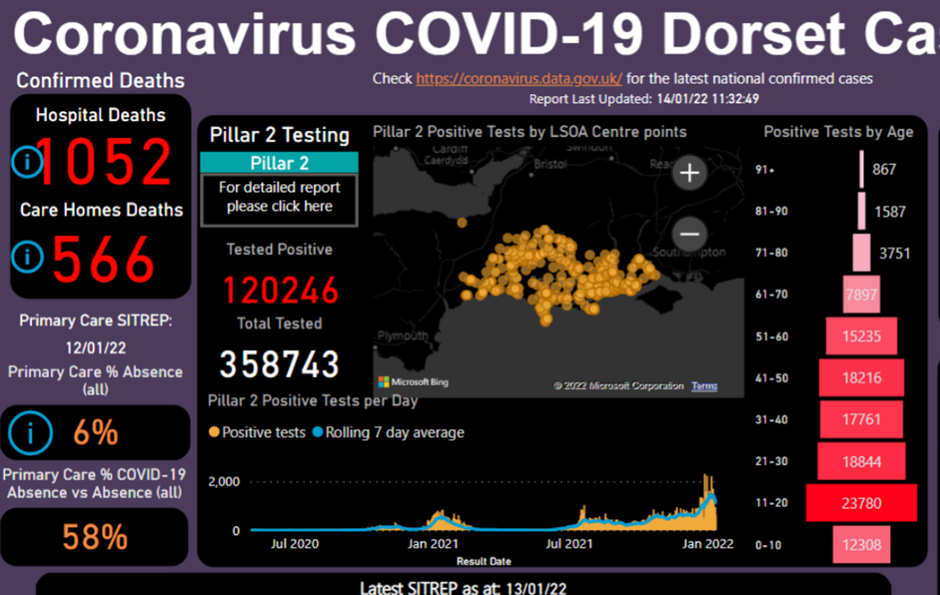
The DIIS Project
The 2020 Dorset DIIS Project: Covid 19 Dashboard
The King’s Fund Covid-19 recovery and resilience curve:
https://features.kingsfund.org.uk/2021/02/covid-19-recovery-resilience-health-care/
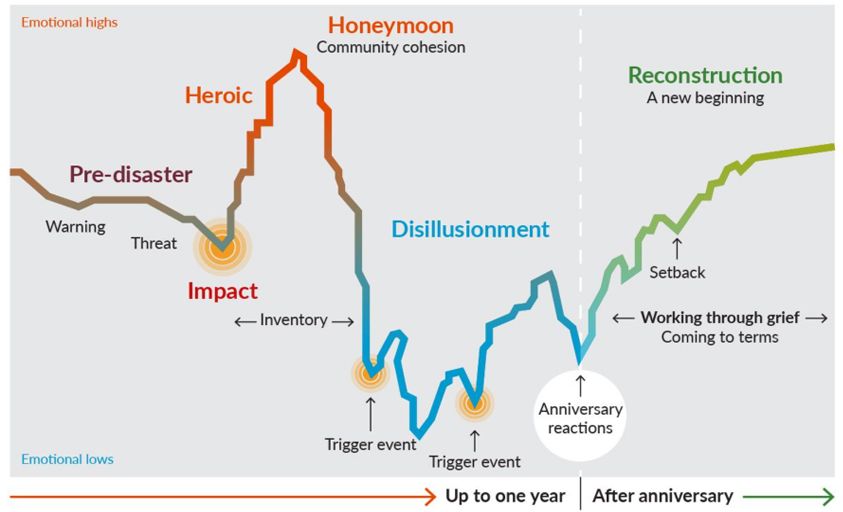
Training Manual for Mental Health and Human Service Workers in Major Disasters. Second Edition.
DeWolfe, Deborah J.
https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED459383
“The Golden Ratio” By Mario Livio
‘Numerology | the Fibonacci sequence, Golden Ratio & Fractals
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kP3yhyZsbjA

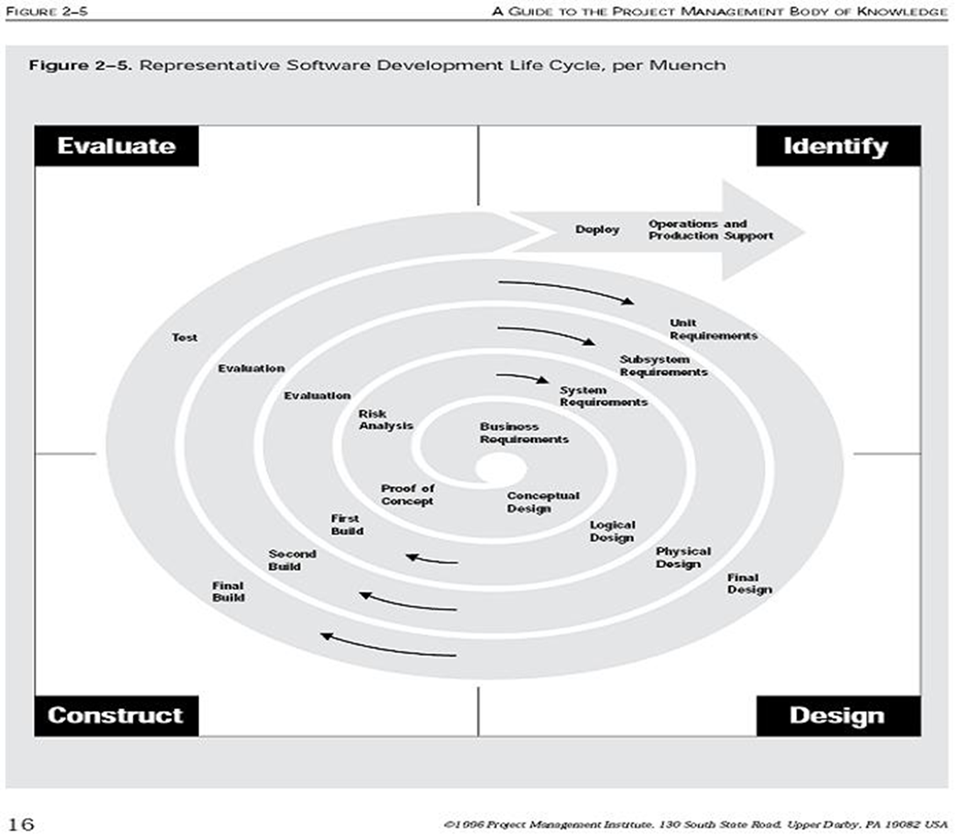
The Spiral Software Development Life Cycle
A systematic and iterative approach to software development.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spiral_model
It is based on the idea of each iteration of the spiral representing a complete software development cycle, from requirements gathering and analysis to design, implementation, testing, and maintenance.